Symptoms of allergy generally vary from person to person ranging from itchiness, hives or rashes, swelling, nausea and vomiting, abdominal cramps and asthma. It is often thought of that these manifestations are triggered by sensitivity to food or medicines to pollens, pets, cosmetics, latex and countless other potential irritants. Allergic symptoms manifest when the body releases histamine to fight off the perceived enemy of foreign element which is the allergen or the irritant.
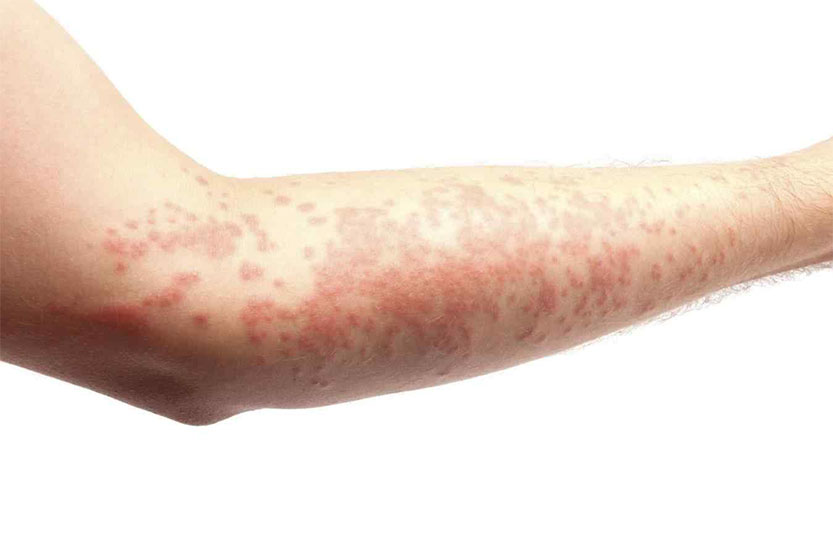
When one has allergies, the symptoms can range from minor discomforts to those that can cause misery and death in extreme cases during a severe allergic reaction known as anaphylaxis or anaphylactic shock. A common manifestation of allergy is urticaria, a skin rash also known as nettle rash or hives.
There are two distinct types of urticaria: acute and chronic urticaria. Acute urticaria is often an indication of an allergy and lasts from hours to six weeks while chronic urticaria has a longer duration of more than six weeks. In most cases, urticaria goes away in a matter of days to several weeks but there are unfortunate individuals who suffer from itchiness and swelling for a period of years.
When one has an outbreak of urticaria, skin lesions and pruritus or body itching occur, and this may be allergic or non-allergic in nature. The rashes appear as red, round or oval bumps on the skin and are often itchy. These rashes are brought about by the release of histamine in the skin causing the small blood vessels near the skin’s surface to leak fluid.
It is this fluid that causes the irritation and swelling or what appears as hives. There are several factors thought of to be contributing to urticaria, and not all of them are due to allergies. The causes of this condition can either be allergens, environmental factors, drugs such as penicillin and emotional factors such as stress.
Another kind of this condition, cholinergic urticaria are hives brought about by profuse sweating, generally a reaction to overheating of the body due to exercise. The hives in cholinergic urticaria are usually small, ranging from 2mm to 3mm and often, they are restricted to the upper torso and the arms although in some cases they manifest in the thighs.
After a rise in body temperature, the hives often develop quickly, usually within 20 minutes of increased internal temperature. These hives which are thought of as a result of exercise or stress dissipate on their own in a matter of 30 minutes. In severe cases, urticaria may be accompanied by lightheadedness, headaches, shortness of breath and abdominal cramps.
The best treatment for cholinergic urticaria by far is taking a cool shower, resting in a cool area or by drinking copious amounts of water. In some cases, the hives can also be instigated by prolonged exposure to sunlight, extreme temperatures and drastic body temperature changes due to the climate.
As for chronic urticaria, the most appropriate treatment would be to address the itching as scratching will only prolong and exacerbate the urticaria outbreak. Calamine lotion may be an effective recourse for this condition as well as oral and topical antihistamines. One can also resort to a variety of herbs having antihistamine properties such as Paeonia and Forsythia extract to accelerate recovery and minimize the itching.
The same can be said about lotions containing green tea to soothe and relieve itchy urticaria hives.
